Abstract
In this paper we present WERITAS, which is based in part on the traditional Active Shape Model (ASM) segmentation
system. WERITAS generates multiple statistical texture features, and finds the optimal weighted average of those texture
features by maximizing the correlation between the Euclidean distance to the ground truth and the Mahalanobis distance
to the training data. The weighted average is used a multi-resolution segmentation system to more accurately detect the
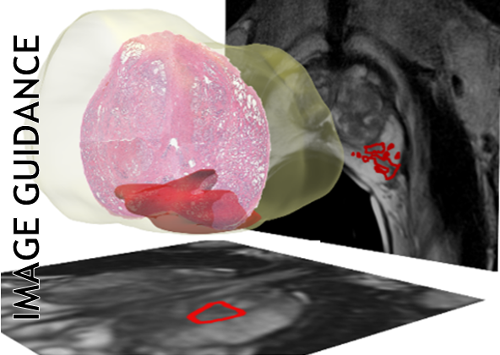
object border. A rigorous evaluation was performed on over 200 clinical images comprising of prostate images and breast
images from 1.5 Tesla and 3 Tesla MRI machines via 6 distinct metrics. WERITAS was tested against a traditional multiresolution ASM in addition to an ASM system which uses a plethora of random features to determine if the selection
of features is improving the results rather than simply the use of multiple features. The results indicate that WERITAS
outperforms all other methods to a high degree of statistical significance. For 1.5T prostate MRI images, the overlap from
WERITAS is 83%, the overlap from the random features is 81%, and the overlap from the traditional ASM is only 66%.
In addition, using 3T prostate MRI images, the overlap from WERITAS is 77%, the overlap from the random features
is 54%, and the overlap from the traditional ASM is 59%, suggesting the usefulness of WERITAS. The only metrics in
which WERITAS was outperformed did not hold any degree of statistical significance. WERITAS is a robust, efficient,
and accurate segmentation system with a wide range of applications.
Link for the publication: https://engineering.case.edu/centers/ccipd/sites/ccipd.case.edu/files/publications/A-Boosted-Ensemble-Scheme-for-Accurate-Landmark-Detection-for-Active-Shape-Models.pdf
To view or download the pdf:
Kalyanpur,A; Toth, R, Doyle; S, Pungavkar; S, Madabhushi, A, “A Boosted multi Scheme for Accurate Landmark Detection for Active Shape Models”, SPIE Medical Imaging, vol. 7260, 2009 (Awarded Michael B. Merickel Best Student Paper award).