Abstract
Segmentation of the prostate boundary on clinical images is useful in a large number of applications including calculating
prostate volume during biopsy, tumor estimation, and treatment planning. Manual segmentation of the prostate boundary
is, however, time consuming and subject to inter- and intra-reader variability. Magnetic Resonance (MR) imaging (MRI)
and MR Spectroscopy (MRS) have recently emerged as promising modalities for detection of prostate cancer in vivo. In
this paper we present a novel scheme for accurate and automated prostate segmentation on in vivo 1.5 Tesla multi-modal
MRI studies. The segmentation algorithm comprises two steps: (1) A hierarchical unsupervised spectral clustering scheme
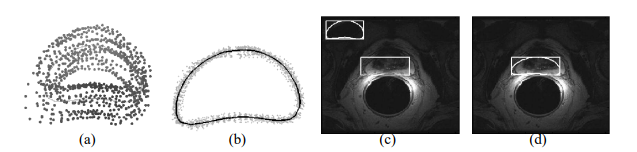
using MRS data to isolate the region of interest (ROI) corresponding to the prostate, and (2) an Active Shape Model
(ASM) segmentation scheme where the ASM is initialized within the ROI obtained in the previous step. The hierarchical
MRS clustering scheme in step 1 identifies spectra corresponding to locations within the prostate in an iterative fashion by
discriminating between potential prostate and non-prostate spectra in a lower dimensional embedding space. The spatial
locations of the prostate spectra so identified are used as the initial ROI for the ASM. The ASM is trained by identifying
user-selected landmarks on the prostate boundary on T2 MRI images. Boundary points on the prostate are identified using
mutual information (MI) as opposed to the traditional Mahalanobis distance, and the trained ASM is deformed to fit the
boundary points so identified. Cross validation on 150 prostate MRI slices yields an average segmentation sensitivity,
specificity, overlap, and positive predictive value of 89%, 86%, 83%, and 93% respectively. We demonstrate that the
accurate initialization of the ASM via the spectral clustering scheme is necessary for automated boundary extraction. Our
method is fully automated, robust to system parameters, and computationally efficient.
Link for the publication: https://engineering.case.edu/centers/ccipd/sites/ccipd.case.edu/files/publications/An-Integrated-Multi-modal-Prostate-Segmentation-Scheme-by-Combining-Magnetic-Resonance-Spectroscopy-and-Active-Shape-Models.pdf
To view or download the pdf: